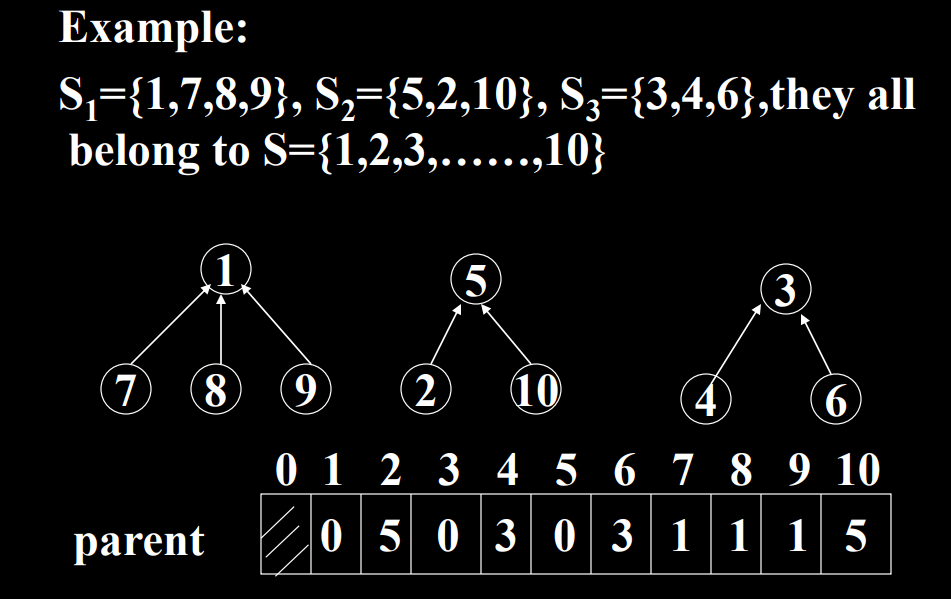
7.1 the disjoint set
1. 等价类
等价类的定义:假设我们有一个n个元素组成的集合U = {1,2,…,n},一个有r个关系的集合R={(i1 ,j1 ), (i2 ,j2 )…… (ir ,jr )}。当且仅当以下条件成立的时候,R才是一个等价类:
- Reflexive x ≡ x.(自反性)
- Symmetric x ≡ y,y ≡ x(对称性)
- Transitive x ≡ y and y ≡ z,then x ≡ z(传递性)
EG
2. 并查集提供的功能
- Combine(a,b):合并包含元素a和b的两个等价类为一个等价类
- Find(e):找到包含元素e的等价类
3. 物理实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
//simple tree solution to union-find problem
//使用简单的树结构解决并集的查找问题
void Initialize(int n){
parent=new int[n+1];
for(int e=1;e<=n;e++) parent[e]=0;
}
int Find(int e) {
//向上找到其根结点
while(parent[e]) e=parent[e];
return e;
}
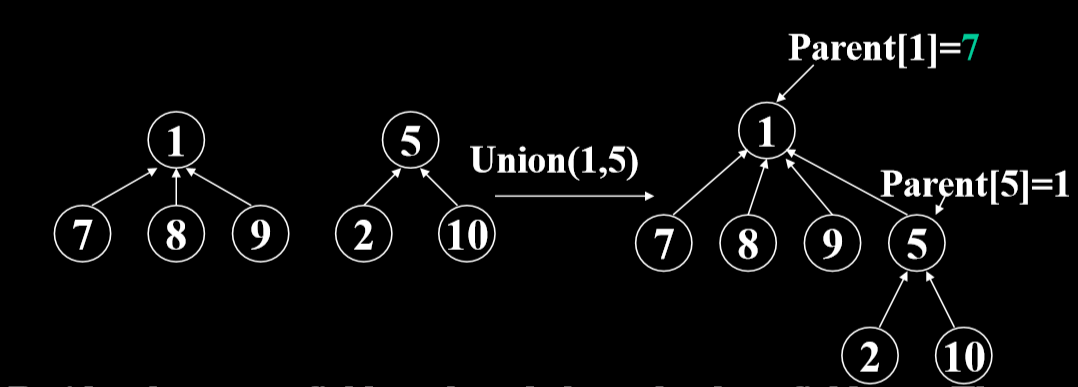
void Union(int i, int j) {
//合并两个结点
parent[j]=i;
}
3.1 并集的实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
public class DisjSets {
public DisjSets( int numElements )
public void union( int root1, int root2 )
public int find( int x ) private int [] s;
}
//并查集的构造方法
public DisjSets( int numElements ) {
s = new int [numElements];
for( int i = 0; i < s.length; i++ )
s[i] = -1; //一个根结点
}
//并查集的合并
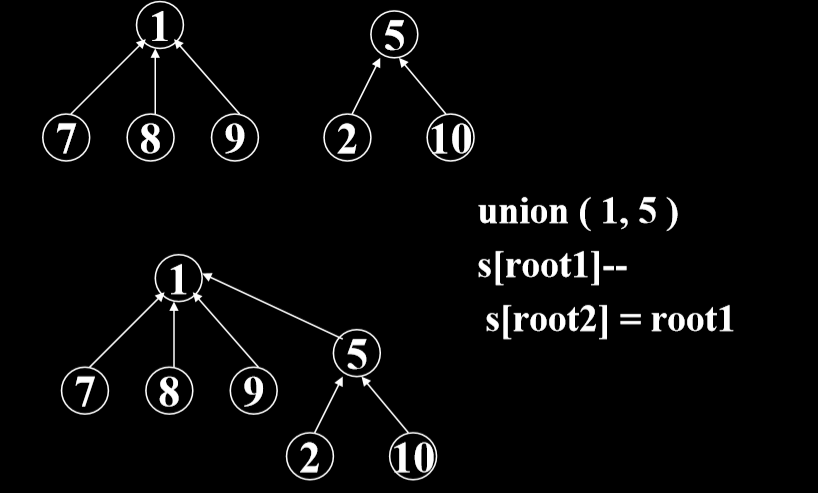
public void union( int root1, int root2 ) {
s[root2] = root1;
}
//并查集的查找,使用递归完成
public int find( int x ) {
if( s[x] < 0 )
return x;
else
return find( s[x] );
}
3.2 性能估计
算法复杂度
- Find– O(h), h 是指树高
- Union– θ(1)
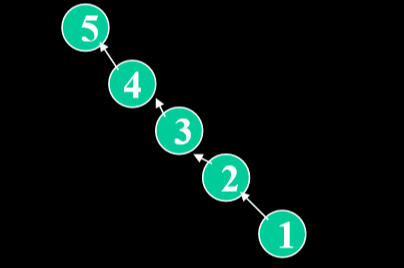
假设我们进行u次组合操作和f次查找操作,f>u,最坏情况下的一颗有m个元素的树可以有高度m
3.3 性能提升
- Weight rule:结点数少的树挂到结点多的树下面
- Height rule:高度低的树挂到高度高的树的下面
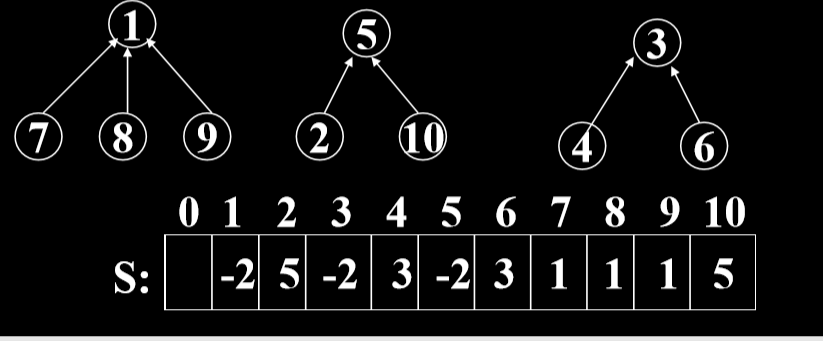
3.3.1 Weight rule
- 根结点的值代表了weight
- 为了实现我们新建一个bool类型数组来记录是否是根节点。
- 除了父字段外,每个节点都有一个布尔字段根。如果当前节点是根节点,则根字段为真。每个根节点的父字段用于统计树中的节点总数。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
//Union with the weight rule
void Initialize(int n) {
root=new bool[n+1];
parent=new int[n+1];
for(int e=1;e<=n;e++) {
parent[e]=1;
root[e]=true;
}
}
int Find(int e) {
while(!root[e])
e=parent[e];
return e;
}
void Union(int i, int j) {
if(parent[i]<parent[j])
//i becomes subtree of j
{
parent[j]=parent[j]+parent[i];
root[i]=false;
parent[i]=j;
} else {
parent[i]=parent[i]+parent[j];
root[j]=false;
parent[j]=i;
}
}
其实也可以省去标记根的数组,用负数来表示weight即可。
3.3.2 Height rule
使用负数来记录树高
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
//java
public void union( int root1, int root2 ) {
if(s[root2] < s[root1])
s[root1] = root2;
else {
if(s[root1] == s[root2] )
s[root1]--;
s[root2] = root1;
}
}//注意到负数会都反过来
3.3.3 find
改进并查集以减少每次查找所需的时间,从而使树的高度不会线性增加
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
//java是用来记录树高
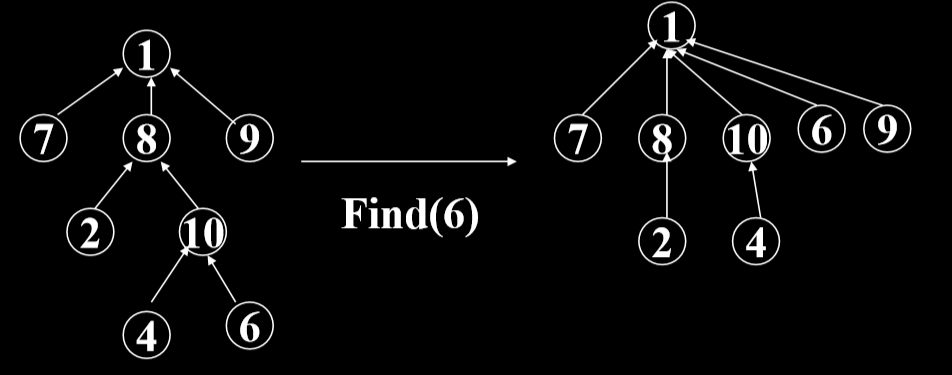
public int find(int x) {
if( s[x] < 0 )
return x;
else
return s[x] = find(s[x]);
}
本文由作者按照 CC BY 4.0 进行授权