6.0 Priority Queues
1. 优先级队列
一个优先级队列是0个或者更多元素的集合。每一个元素都有一个优先级或者值
进入队列的时候有优先级,出队列优先出高优先级的.
以下我们确定元素的优先级是通过数字的大小来确定。
1.1 优先级队列分类(根据大小)
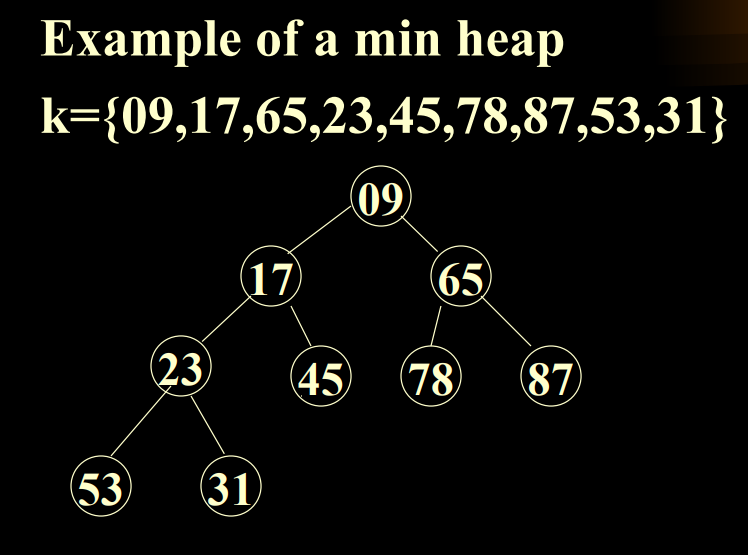
- 在最小优先级队列(min priority queue)中,当需要删除一个元素的时候,我们找到优先级最小的元素来删除
- 在最大优先级队列(max priority queue)中,当需要删除一个元素的时候,我们找到优先级最大的元素来删除
2. 最大优先级队列
2.1 ADT
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
AbstractDataType MaxPriorityQueue
{
//有限的元素的结合,每个元素都有一个优先级
Create(): create an empty priority queue //创建一个空的优先级队列
Size(): return number of element in the queue //返回队列中元素的个数
Max(): return element with maximum priority //返回队列中拥有最高优先级的元素
Insert(x): insert x into queue //插入x进入队列
DeleteMax(x):delete the element with largest priority from the queue; return it in x;//删除队列中最高优先级的元素,并且通过x返回它
}
实现:
- 用无序线性表来进行实现
- 插入元素到链表的最右边(时间复杂度为θ(1))
- 需要查找到最高优先级的元素并且删除这个元素(时间复杂度为θ(n))
2.2 物理实现:Heap(堆)
2.2.1 Heap
- 堆中某个节点的值总是不大于或不小于其父节点的值(每一个节点上的值都大于(小于)或者等于他的子节点(如果有的话))
- 堆总是一棵完全二叉树
将根节点最大的堆叫做最大堆或大根堆,根节点最小的堆叫做最小堆或小根堆。
2.2.2 实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
template<class T>class MaxHeap
{
public:
MaxHeap(int MaxHeapSize=10);
~MaxHeap(){delete[]heap;}
int size()const{return CurrentSize;}
T Max(){
if (CurrentSize==0) throw OutOfBounds();
return heap[1];
}
MaxHeap<T>&insert(const T&x);
MaxHeap<T>& DeleteMax(T& x);
void initialize(T a[], int size, int ArraySize);
private:
int CurrentSize, MaxSize;
T * heap;
}
注:数组0号位置不用,也就是从Heap[1]开始使用
使用的堆是基于数组的,并没有创建一个真正的二叉树。
2.2.3 构造函数
1
2
3
4
5
template<class T> MaxHeap<T>::MaxHeap(int MaxHeapSize) {
MaxSize=MaxHeapSize;
Heap = new T[MaxSize+1];
CurrentSize=0;
}
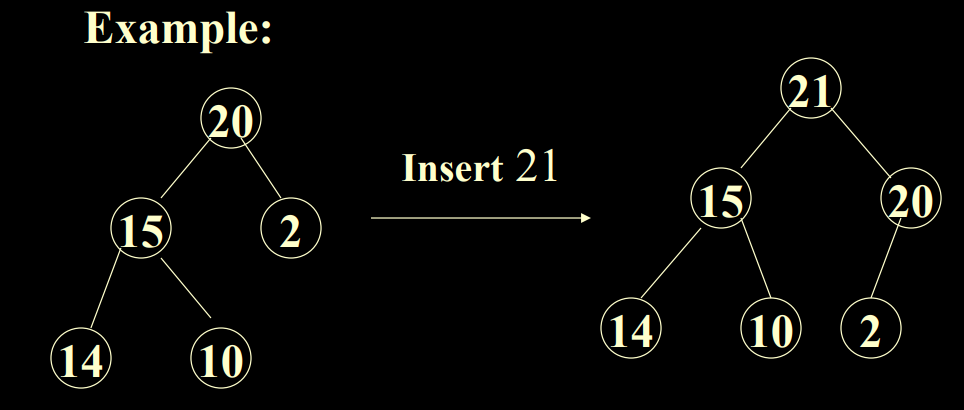
2.2.4 插入算法
在数组后面插入后,和其父结点进行比较,如果比父结点大,则交换,一直到不再大于其父结点
堆数组类似于下图:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
template<class T>MaxHeap<T>& MaxHeap<T>:: Insert(const T& x){
if(CurrentSize= =MaxSize) throw NoMem();
int i=++CurrentSize;
while(i!=1 && x>heap[i/2]){
//0不使用
heap[i]=heap[i/2];
//不必每次都进行完全交换
i/=2;
}
heap[i]=x;
return *this;
}
时间复杂度:O(logn)
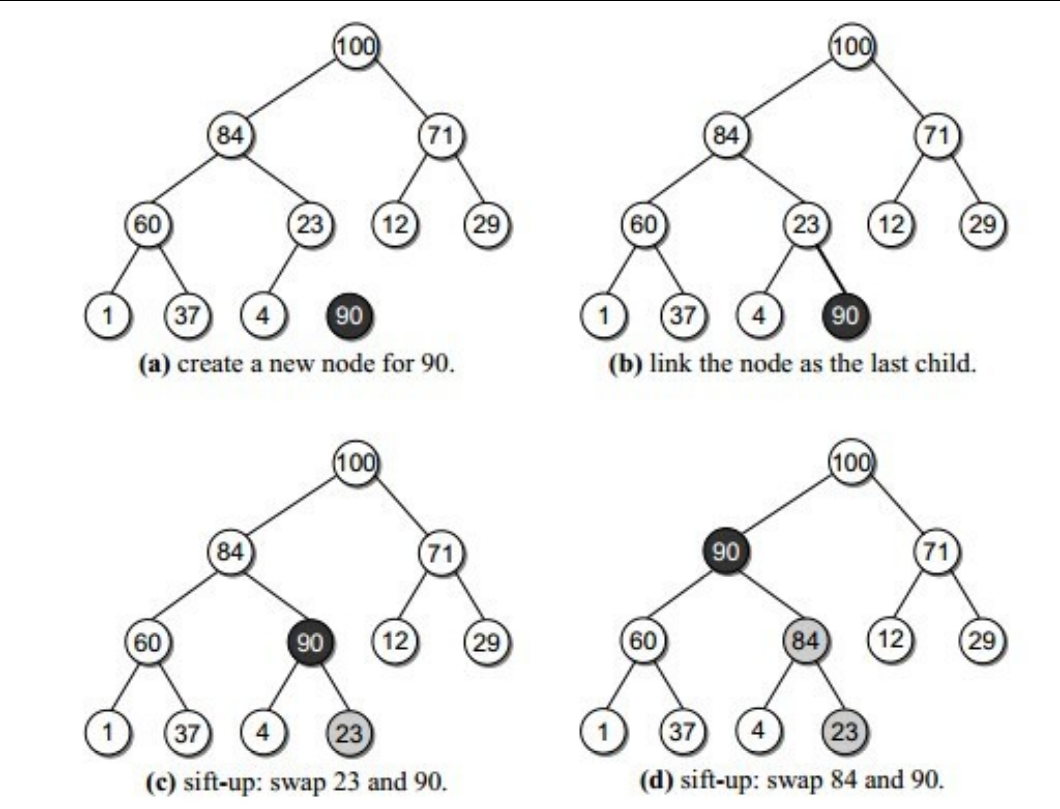
2.2.5 删除算法
只需要删除根(显而易见)
将根删除,将数组最后一个(最后一层最后一个元素)换为根,然后进行比较。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
template<class T>MaxHeap<T>& MaxHeap<T>:: DeleteMax(T& x){
if(CurrentSize==0) throw OutOfBounds();
x = heap[1];
//0无存储,这个就是root结点
T y=heap[CurrentSize--];//最后一个结点
int i=1;//i标向树根
ci=2;//ci先标到左子树
while(ci<=CurrentSize){
if(ci<CurrentSize && heap[ci]<heap[ci+1]){
//如果ci未越界,并且左子树的值小于右子树的值。
//找个大的和根换
ci++;//转向右子树
}
if(y>=heap[ci]) break;
heap[i]=heap[ci];
i=ci;
ci*=2;
}
heap[i]=y;//y是最后一个节点
return *this;
}
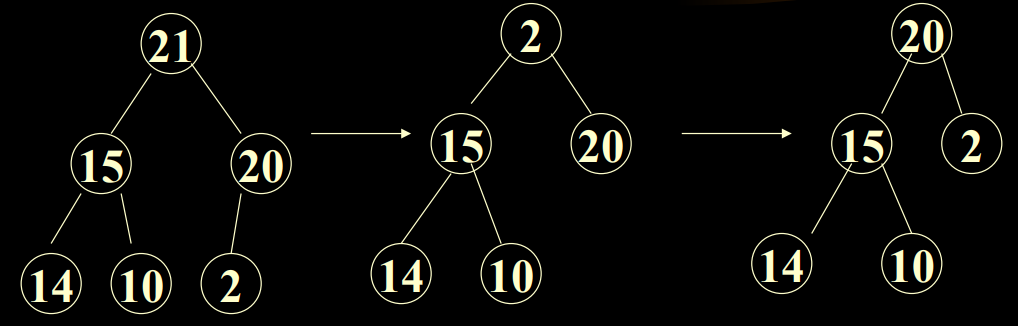
注:代码的做法,似乎和上图不一样。
代码的图:
21 20 20
15 20 ——> 15 20 ——> 15 20 ——> 15 2
14 10 2 14 10 2 14 10 2 14 10
时间复杂度:O(logn)
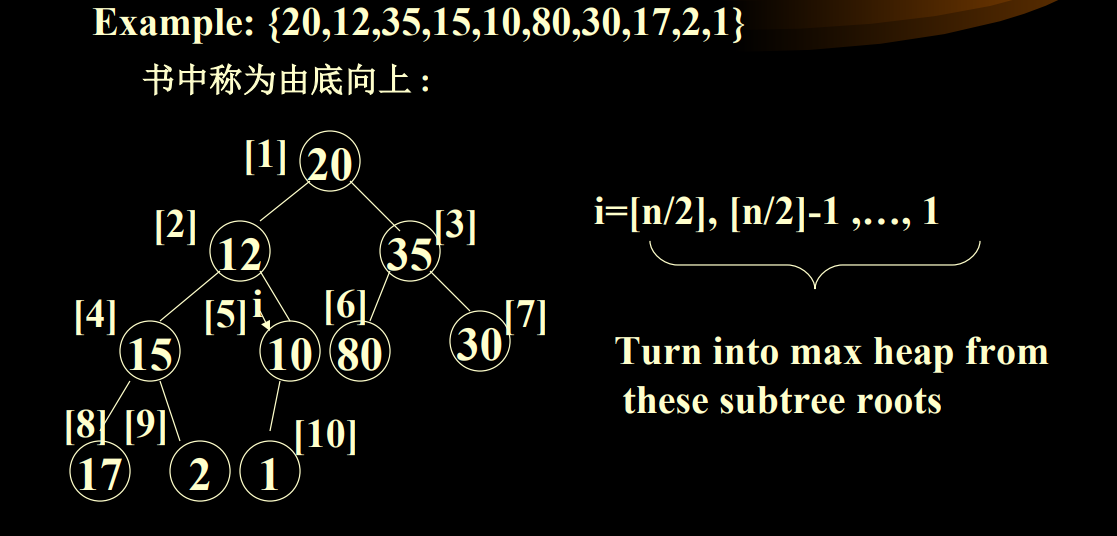
2.2.6 初始化一个非空的最大优先级数列
由底向上:
- 把初始指针指向最后一个节点的父结点(N/2),然后向前循环
- 从最后一个节点的父结点开始(这样就可以保证所有非叶结点都可以操作到),对所有的非叶节点进行下滤操作
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
//C++
//注意是对每个子树进行递归处理
Template<class T> void MaxHeap<T>::Initialize (T a[],int size,int ArraySize) {
delete[] heap;
heap=a;
CurrentSize=Size;
MaxSize=ArraySize;
for( int i=CurrentSize/2; i>=1; i--) {
T y=heap[i];
//c为i的子树位置
int c=2*i;
while(c <= CurrentSize){
//左右子树中找大的
if(c<CurrentSize && heap[c]<heap[c+1])
c = c+1;
if(y>=heap[c])
break;
//根比子树小,就向下传动
heap[c/2] = heap[c];
c*=2;
//找到其子节点位置
}
heap[c/2]=y;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
// java
private void buildHeap(){
for( int i = currentSize / 2; i > 0 ; i-- )
percolateDown(i);
}
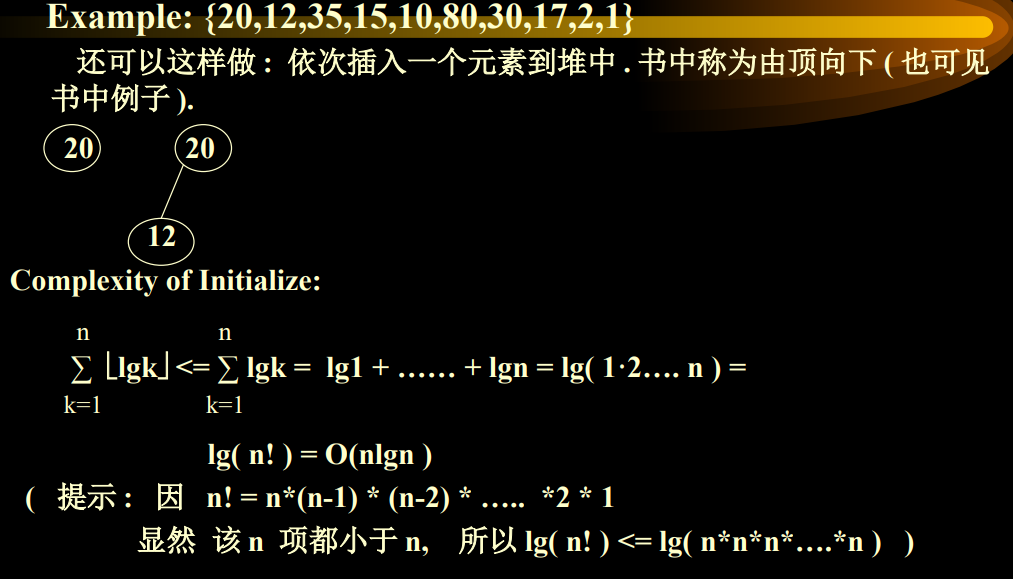
复杂度分析:
“第i层交换的最大次数为k-i”的意思是“第i层的每一个元素交换的最大次数为k-i”
时间复杂度:O(n)
由顶向下:逐个做插入操作即可
时间复杂度:O(n logn)
3. 最小优先级队列
3.1 ADT
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
public class BinaryHeap {
public BinaryHeap( )
public BinaryHeap( int capacity )
public void insert( Comparable x ) throws Overflow()
public Comparable findMin( )
public Comparable deleteMin( )
public boolean isEmpty( )
public boolean isFull( )
public void makeEmpty( )
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 100
private int currentSize
private Comparable [ ] array;
private void percolateDown( int hole )
private void buildHeap( )
}
public BinaryHeap(){
this( DEFAULT_CAPACITY );
}
public BinaryHeap( int capacity ) {
currentSize = 0;
array = new Comparable[ capacity + 1 ];
}
public void makeEmpty( ) {
currentSize = 0;
}
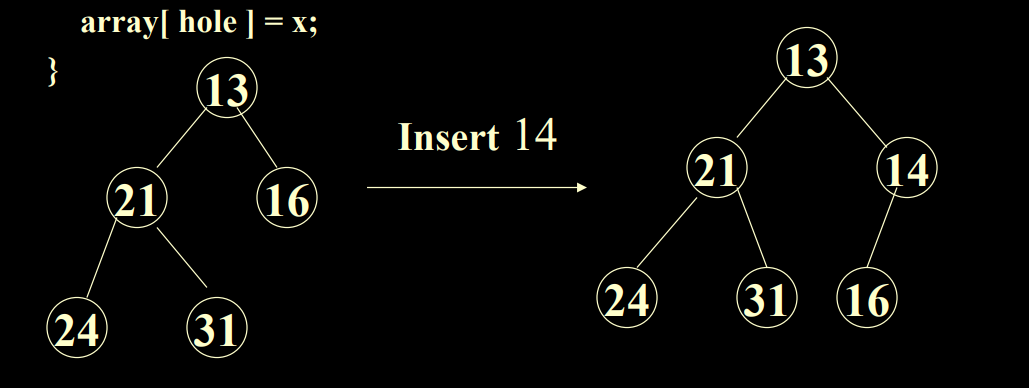
3.2 插入算法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
//最小堆的插入算法
public void insert( Comparable x ) throws Overflow() {
if(isFull()) throw new Overflow();
int hole = ++currentSize;
for(;hole>1 && x.comparebleTo(array[hole/2])<0;hole/= 2){
array[hole] = array[hole / 2];
}
array[ hole ] = x;
}
3.3 删除算法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
public Comparable deleteMin(){
if( isEmpty()) return null;
Comparable minItem = findMin( );
array[1] = array[currentSize--];
percolateDown(1);
return minItem;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
//最小堆的,将hole下标的元素向下传动,下滤算法
private void percolateDown(int hole) {
int child;
Comparable tmp = array[hole];
for(;hole*2<=currentSize;hole = child) {
child = hole * 2;//切入到左子树
if(child!=currentSize && array[child+1 ].compareTo(array[child])<0)
child++;//如果没有到头,并且右子树比左子树小,则转向右边的子树
if(array[child].compareTo(tmp)<0)
array[hole] = array[child];//如果小则进行交换
else
break;
}
array[hole] = tmp;
}
4. 应用
4.1 堆排序
- 初始化一个n个元素的最大堆,O(n)
每次我们删除最大的元素,调整堆的时间复杂度为O(log2n)
- 将待排序的序列构造成一个最大堆,此时序列的最大值为根节点
- 依次将根节点与待排序序列的最后一个元素交换
- 再维护从根节点到该元素的前一个节点为最大堆,如此往复,最终得到一个递增序列
时间复杂度:O(n) + O(nlogn)(每一个结点都会被删除,所以是n * logn) = O(n logn)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
//c++
Template<class Type>void HeapSort(datalist<Type>&list){
for(int i=(list.currentsize)/2;i>=1;i--)
FilterDown(i,list.currentsize);
for(i=list.currentsize; i>1 ;i--){
Swap(list.Vector[1],list.vector[i]);
FilterDown(1,i-1);
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
//java
public static void heapsort( Comparable [] a ) {
for( int i = a.length / 2; i >= 1; i-- )
percDown( a, i, a.length );
for( int i = a.length ; i > 1; i-- ) {
swapReferences(a,1,i);
percDown(a,1,i-1);
}
}
private static void percDown( Comparable [] a, int i, int n ) {
int child;
Comparable tmp;
for( tmp = a[ i ]; leftChild( i ) < n; i = child ) {
child = leftChild( i );
if( child != n – 1 && a[child ].compareTo( a[ child + 1 ]) < 0 )
child++;
if( tmp.compareTo( a[ child ] ) < 0 )
a[ i ] = a[ child ];
else break;
}
a[ i ] = tmp;
}
private static int leftChild( int i ) {
return 2 * i + 1;
}
我认为根本不用这么烦,可以直接调用删除算法
5. 例题
答案:A
本文由作者按照 CC BY 4.0 进行授权