5.0 Hashing 哈希
1. 散列表 (Hash Table )
Address = hash(key)
设计目标:散列函数的复杂度理论上能够到达常数级别复杂度。
总体思路:给一个key,能找到value。那就需要有一个从key到地址的映射。
- 桶(Bucket): 桶是哈希表中的存储单元,通常是一个数组。每个桶可以存储一个或多个键值对。哈希表使用哈希函数将键映射到特定的桶。当发生哈希冲突时,即两个或更多键映射到同一个桶,解决冲突的方式可能包括使用链表、树等数据结构将多个键值对存储在同一个桶中。
- 元素(Element): 元素是指哈希表中存储的键值对。每个元素包含一个键和对应的值。元素被存储在桶中,通过哈希函数确定存储的桶的位置。在哈希表中,我们通常使用键来查找对应的值。
假设我们有一个存储学生信息的哈希表,其中键是学生的学号,值是学生的姓名。这个哈希表有10个桶(桶的数量通常是根据哈希表的大小确定的)。
哈希表: Bucket 0: [ ] Bucket 1: [ ] Bucket 2: [ ] Bucket 3: [ ] Bucket 4: [ ] Bucket 5: [ ] Bucket 6: [ ] Bucket 7: [ ] Bucket 8: [ ] Bucket 9: [ ]
并且我们使用以下哈希函数:
hash(key) = key % 5现在,考虑以下两个键值对发生了哈希冲突,它们都映射到了同一个桶:
- 键: 3,值: “Alice”
- 键: 8,值: “Bob”
键3和键8都映射到了桶3。
此时,桶3的状态可能是一个链表(或是一个数组,总之是线性表),如下所示:
Bucket 3: [ (3, “Alice”) -> (8, “Bob”) ]
在这个例子中,桶3中有两个元素,它们通过链表连接在一起。当需要查找键为3或8的值时,哈希表会在桶3的链表中进行线性搜索,直到找到相应的键值对。
这是一种简单的处理哈希冲突的方式。其他方法可能包括使用开放寻址法、二次探查等。
1.1 散列函数
1.1.1 如何寻找合适的散列函数
冲突选择合适的负载因子α=n/b
n:element的数量
b:bucket的数量
α > 1 碰撞频率大 α< 1 碰撞频率小
1.1.2 取余法
取最大质数:键可以被更均匀地分布到不同的桶中,减少了哈希冲突的概率。
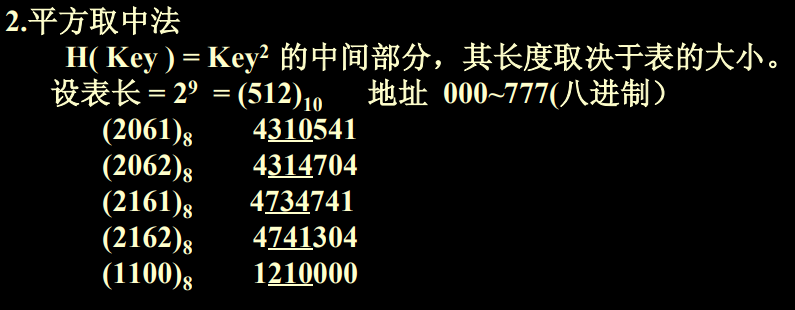
1.1.3 平方取中法
- 先进行原来的数据进行平方,然后选取中间的合适部分。
- 对于一个值,按照某一进制下进行处理,处理后选择其中合适的中间部分。(类字符串进行存取)
1.1.4 乘法杂凑函数
%1是留下小数部分
例子中fai取了0.618
1.1.5 针对字符串-1
把字符串中的每一个字符的ASCII值或者Unicode值相加(再取模)
1
2
3
4
5
6
public static int hash( String Key, int tableSize ) {
int hashVal = 0;
for( int i = 0; i < Key.length( ); i++ )
hashVal += Key.charAt( i );
return hashVal % tableSize;
}
TableSize = 10007, 如果所有key小于等于8个char, 8*127=1016,那hash函数只能有0-1016的结果,大大滴浪费。
字符串远远短于散列表的大小时,会导致浪费。
1.1.6 针对字符串-2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
public static int hash( String key, int tableSize ){ // good hash fanction
int hashVal = 0;
for( int i = key.length( )-1; i > =0; i-- )
hashVal = 37 * hashVal + key.charAt( i );
hashVal %= tableSize;
if( hashVal < 0 ) // 函数允许溢出,这可能会引进负数
hashVal += tableSize;
return hashVal;
}
对于每一个char,前面多一个系数。
1.2 如何解决散列表冲突问题
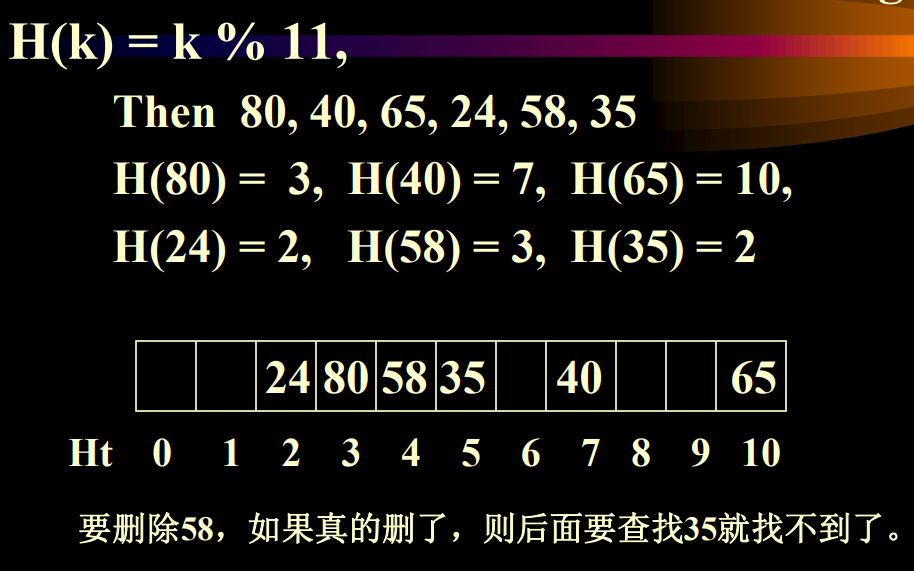
碰撞的两个(或多个)关键码称为同义词, 即H(k1) = H(k2), k1不等于k2
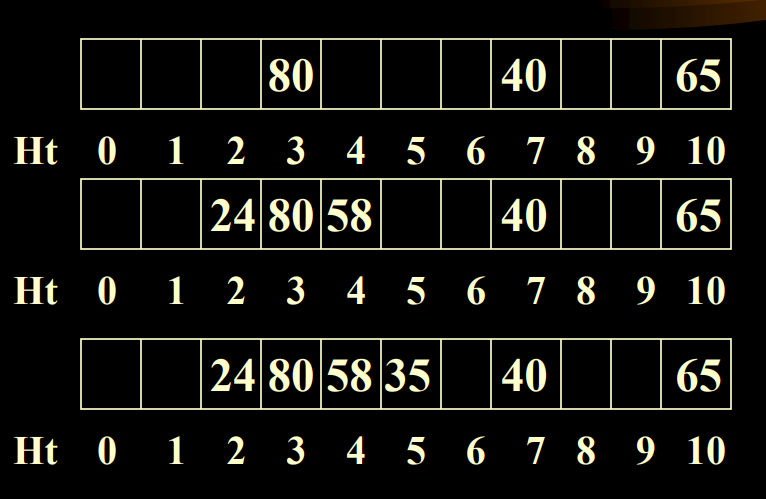
1.2.1 线性探测法(linear Probing)
如果key的哈希值是d,并且d对应的位置已经被占据,然后我们会按照线性顺序向后成环形查找
也就是向后塞
平均成功访问次数:
问题:堆积问题(clustering problem):指不同的同义词表合为一张了。从而增加了插入,查找的时间。
这个方法也太二逼了
1.2.2 二次探测法(Quadratic probing)
如果H(k)已经被占据了,那就去以线性的顺序去找d + 1, d + 22, d + 32 ……
1.2.3 双散列哈希(Double Hashing)
第一个散列函数发生冲突,那么使用第二个散列函数来放置,如果再次冲突则进行相应探测。
如果k的第一哈希值为d,而这个对应的格子已经被占用,则我们继续计算k的第二哈希值,然后检查d+c,d+2c, d+3c…
再散列(进行扩容):当表项数 > 表的70% 时,可再散列。 即, 取比(2*原表长=14)大的质数17再散列。
6%17=6, 15%17=15, 23%17=6, 24%17=7, 13%17=13
(右边的键值有点乱,不用介意)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
private void rehash(){
HashEntry [] oldArray = array ;
allocateArray(nextPrime(2*oldArray.length));
currentSize = 0;
for( int i = 0;i < oldArray.length;i++ )
if(oldArray[i] != null && oldArray[i].isActive)
insert(oldArray[i].Element);
}
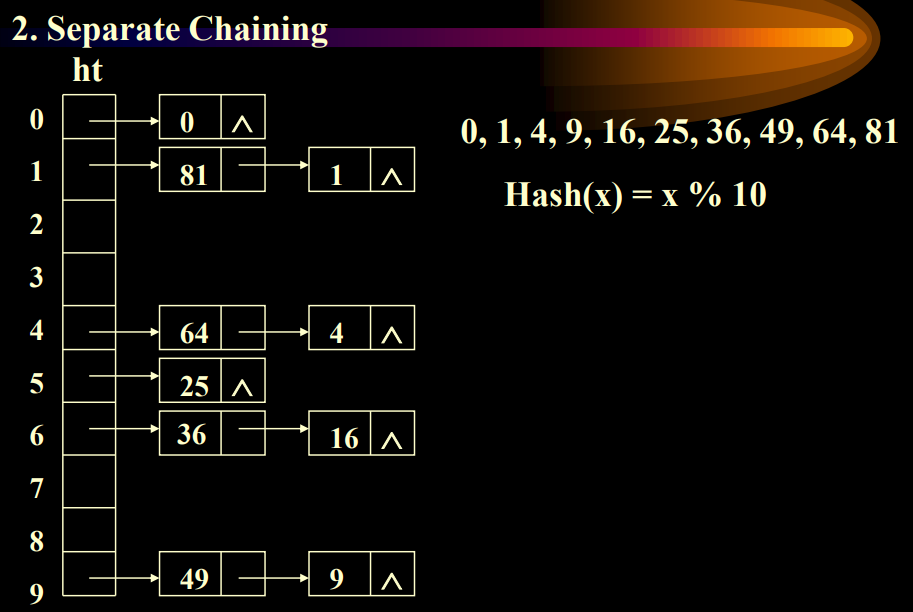
1.2.4 分离链接法(Separate Chaining)
使用每个位置对应线性表解决这个问题
避免了向后顺延。
1.4 实现
1.4.1 散列表的c++实现
- 我们假设存储在散列表中的每一元素的类型是E,并且有一个类型为k的关键码
- 散列表的实现使用了两个数组,一个是ht(也就是bucket),另一个是empty
- ht[t]中含有element当且仅当empty[i]是true
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
template<class E,class K>
class HashTable{
public:
HashTable(int divisor =11);
~HashTable(){
delete[]ht;
delete []empty;
}
bool Search(const K&k ,E& e)const;
HashTable<E,K>&Insert(const E&e);
private:
int hSearch(const K& k)const;
int D;//hash function divisor
E *ht ; //hash table array
bool *empty ; //1D array
};
1.4.2 线性探测法的c++实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
//hashtable的构造方法
template<class E,class K>//E和K需要被实例化后,这个类才能被调用。
HashTable<E,K>::HashTable(int divisor){
D = divisor;
ht = new E[D];
empty= new bool[D];
for(int i=0;i<D;i++)
empty[i] = true;
}
template<class E,class K>
int HashTable<E,K>::hSearch(const K&k)const {
int i= % D;//home bucket
int j= i ; //start at home bucket
do {
if(empty[j] || ht[j]==k) return j;//fit
j=(j+1)%D; //next bucket
} while(j!= i); //returned to home?是否循环完成一遍
return j; //table full;
}
//参数进行引用K&k
template<class E,class K>
bool HashTable<E,K>::Search(const K&k,E&e)const{
//put element that matches k in e.
//return false if no match.
int b= hSearch(k);
if(empty[b]||Hash(ht[b])!=k)return false;
e=ht[b];
return true;
}
template<class E,class K>
HashTable<E,K>& HashTable<E,K>::Insert(const E& e) {
K k=Hash(e);//extract key
int b=hSearch(k);
if(empty[b]){
empty[b]=false;
ht[b]=e;
return *this;
}
throw NoMem(); //table full
}
1.4.3 二次探测法的java实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
public interface Hashable {
int hash(int tableSize);
}
class HashEntry {
Hashable element;
boolean isActive;
public HashEntry(Hashable e){this(e, true);
}
public HashEntry(Hashable e, boolean i) {
this.element = e;
this.isActive = i;
}
}
public class QuadraticProbingHashTable {
public QuadraticProbingHashable()
public QuadraticProbingHashable(int size)
public void makeEmpty( )
public Hashable find(Hashable x)
public void insert(Hashable x)
public void remove(Hashable x)
public static int hash(String key, int tableSize)
private static final int DEFAULT_TABLE_SIZE = 11;
protected HashEntry [ ] array; private int currentSize;
private void allocateArray(int arraySize )
private boolean isActive( int currentPos )
private int findPos( Hashable x )
private void rehash( )//需要扩大hash表大小的时候,再哈希
private static int nextPrime( int n )
private static boolean isPrime( int n )
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
//构造方法
public QuadraticProbingHashTable( ) {
this( DEFAULT_TABLE_SIZE );
}
public QuadraticProbingHashTable( int size ) {
allocateArray( size );
makeEmpty( );
}
//其他方法
private void allocateArray(int arraySize){
array = new HashEntry[arraySize];
}
//清空哈希表
public void makeEmpty() {
currentSize = 0;
for( int i = 0; i < array.length; i++ )
array[ i ] = null;
}
//查找哈希表元素
public Hashable find(Hashable x) {
int currentPos = findPos(x);
return isActive(currentPos)?array[currentPos].element:null;
}
private int findPos(Hashable x) {
int collisionNum = 0;
int currentPos = x.hash(array.length);
while(array[currentPos] != null && !array[currentPos].element.equals(x)) {
currentPos += 2*collisionNum – 1;//二次探测法 n2 - (n-1)2= 2n-1
if(currentPos >= array.length)
currentPos -= array.length;
}//如果已经放满,并且要找的值不在里面会进入死循环
return currentPos;
}
private boolean isActive( int currentPos ) {
return array[currentPos]!=null && array[ currentPos ].isActive;
}
public void insert(Hashable x) {
int currentPos = findPos(x);
if(isActive(currentPos))
return;
array[currentPos] = new HashEntry( x, true );
if( ++currentSize > array.length/2)
rehash();
}
public final void remove(Hashable x) {
int currentPos = findPos(x);
if(isActive(currentPos))
array[currentPos].isActive = false;
}
1.4.4 分离连接法的java实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
public class SeparateChainingHashTable {
public SeparateChainingHashTable( )
public SeparateChainingHashTable( int size )
public void insert( Hashable x )
public void remove( Hashable x )
public Hashable find( Hashable x )
public void makeEmpty( )
public static int hash( String key, int tableSize )
private static final int DEFAULT_TABLE_SIZE = 101;
private LinkedList [] theLists;
private static int nextPrime( int n )
private static boolean isPrime( int n )
}
public interface Hashable{
int hash( int tableSize );
}
public class Employee implements Hashable {
public int hash( int tableSize ) {
return SeparateChainingHashTable.hash( name, tableSize );
}
public boolean equals( object rhs ) {
return name.equals( ( Employee) rhs ).name );
}
private String name;
private double salary;
private int seniority;
}
public SeparateChainingHashTable() {
this( DEFAULT_TABLE_SIZE );
}
public SeparateChainingHashTable(int size) {
theLists = new LinkedList[ nextPrime( size ) ];
for( int i = 0; i < theLists.length; i++ ) theLists[ i ] = new LinkedList( );
}
public void makeEmpty( ) {
for( int i = 0; i < theLists.length; i++ )
theLists[ i ].makeEmpty( );
}
public void remove( Hashable x ){
theLists[ x.hash( theLists.length ) ].remove( x );
}
public Hashable find( Hashable x ) {
return ( Hashable ) theLists[ x.hash( theLists.length ) ]. Find( x ). Retrieve( );
}
public void insert( Hashable x ) {
LinkedList whichList = theLists[ x.hash( theLists.length ) ];
LinkedListItr itr = whichList.find( x );
if( itr.isPastEnd( ) )
whichList.insert( x, whichList.zeroth( ) );
}