4.1 Specific Trees 搜索树
1. Binary Search Trees 二叉搜索树
二叉搜索树是一个可以为空的二叉树。一个非空的二叉树都满足如下性质:
- 每一个元素都含有一个关键字,并且每一个元素都有独一无二的关键字
- 一个树的左子树的关键字小于根中的关键字
- 一个树的右子树的关键字大于根中的关键字
- 根的左右子树还是二叉搜索树
二叉搜索树需要满足的事情:在很大的数据量下,要能够很快的进行增删查改。这也就是二叉搜索树的优越性。
1.1 Indexed Binary Search Tree 索引二叉搜索树
- 索引二叉搜索树是从普通二叉搜索树衍生 而来的,方法是在每个树节点上添加字段 leftSize。
- Leftsize 字段中的值=节点左侧子树的元素个数 +1
1.2 二叉搜索树的实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
class BinaryNode {
BinaryNode( Comparable theElement ) {
this( theElement, null, null );//调用本类中的其他构造方法
}
BinaryNode( Comparable theElement, BinaryNode lt,BinaryNode rt ) {
element = theElement
left = lt;
right = rt;
}
Comparable element;
BinaryNode left;
BinaryNode right;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
//二叉搜素树的实现
public class BinarySearchTree {
public BinarySearchTree(){ root = null; }
public void makeEmpty(){ root = null; }
public boolean isEmpty(){ return root == null;}
public Comparable find( Comparable x )
{return elementAt( find( x, root));}
public Comparable findMin()
{return elementAt( findMin( root ) );}
public Comparable findMax()
{return elementAt( findMax( root ) );
public void insert( Comparable x )
{root = insert( x, root );}
public void remove( Comparable x ) {root = remove( x, root ); }
public void printTree()//都是外部接口
private BinaryNode root;
private Comparable elementAt( BinaryNode t ){ return t == null ? Null : t.element; }
private BinaryNode find( Comparable x, BinaryNode t )
private BinaryNode findMin( BinaryNode t )
private BinaryNode findMax( BinaryNode t )
private BinaryNode insert( Comparable x, BinaryNode t )
private BinaryNode remove( Comparable x, BinaryNode t )
private BinaryNode removeMin( BinaryNode t )
private void printTree( BinaryNode t )
}
//查找某个元素的算法
private BinaryNode find( Comparable x, BinaryNode t ) {
if( t == null )
return null;
if( x.compareTo( t.element ) < 0 )
return find( x, t.left );
else if( x.compareTo( t.element ) > 0 )
return find( x, t.right );
else
return t;//Match
}
//查找值最小的结点
//使用递归查找结点
private BinaryNode findMin( BinaryNode t ) {
if( t == null )
return null;
else if( t.left == null )
return t;
return findMin( t.left );
}
//迭代找最小结点
private BinaryNode findMin(BinaryNode t){
if(t != null){
while(t.left != null){
t = t.left;
}
}
return t;
}
//递归找到最大结点
private BinaryNode findMax( BinaryNode t){
if(t == null){
return null;
}else if(t.right == null){
return t;
}
return findMax(t.right);
}
//迭代找到最大结点
private BinaryNode findMax( BinaryNode t ) {
if( t != null )
while( t.right != null )
t = t.right;
return t;
}
//将数值插入固定位置的算法
private BinaryNode insert( Comparable x, BinaryNode t ) {
//先查找一次,如果找到了就不用进行查找
if( t == null )
t = new BinaryNode( x, null, null );
else if( x.compareTo( t.element ) < 0 )
t.left = insert( x, t.left );
else if( x.compareTo( t.element ) > 0 )
t.right = insert( x, t.right );
else ;//duplicate; do nothing
return t;
}
//compareTo()方法如果小于返回负数,大于返回正数
插入示意图:
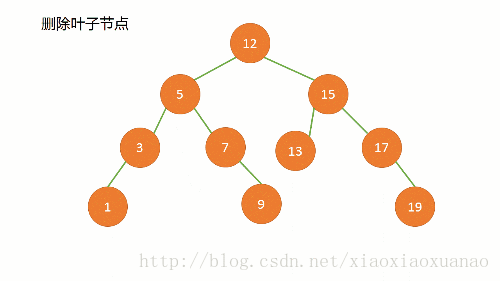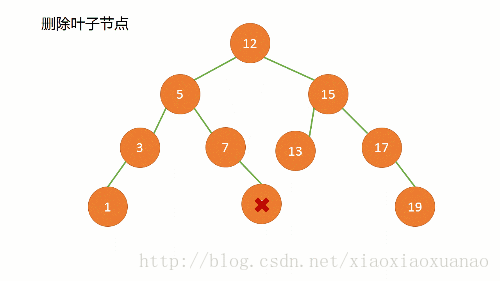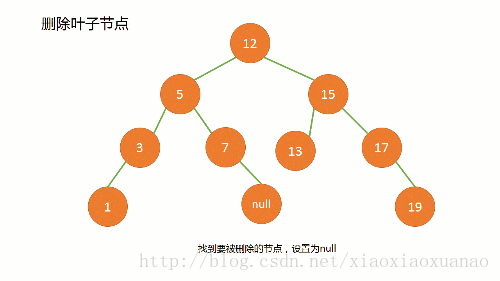
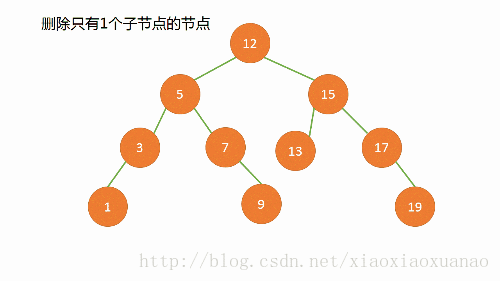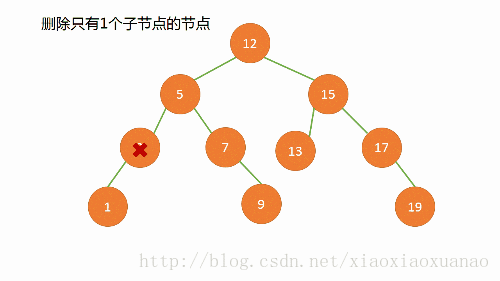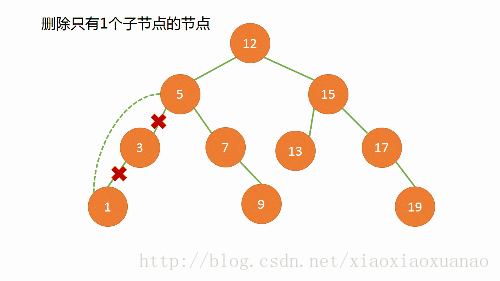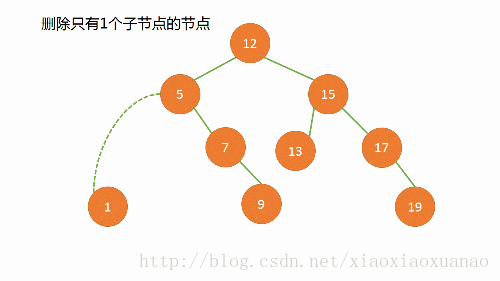
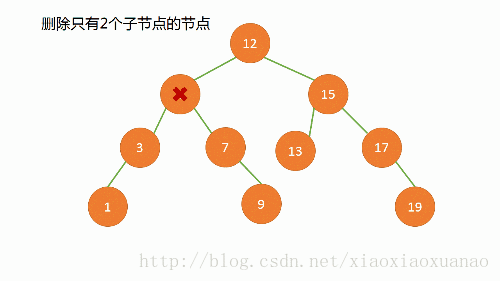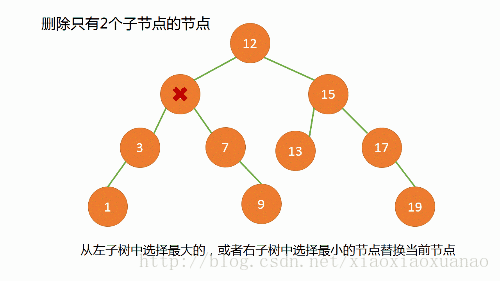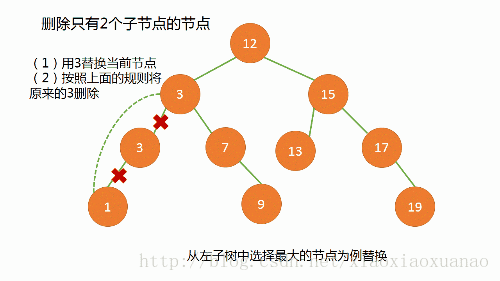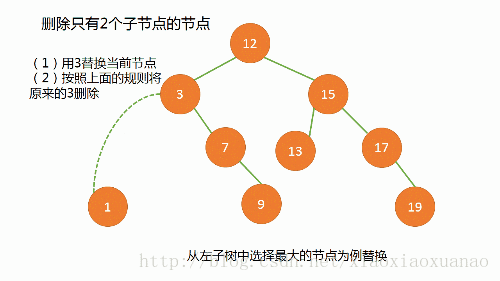
1.2.1 删除算法
如果结点本身不在树内,那么不需要删除
如果结点本身在树里面,删除需要分类
无子树:删除叶节点
一颗子树:直接连接
两颗子树:找出左子树中最大或者右子树中最小的结点作为新结点
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
private BinaryNode remove( Comparable x, BinaryNode t ) { if( t == null ) return t; if( x.compareTo( t.element ) < 0 ) t.left = remove( x, t.left ); else if( x.compareTo( t.element ) > 0 ) t.right = remove( x, t.right ); else if( t.left != null && t.right != null ) { t.element = findMin( t.right ).element;//把右树最小的复制给t t.right = remove( t.element , t.right );//递归的删除 }else{ t = ( t.left != null ) ? t.left : t.right;//一颗子树的情况 } return t; }
1.3 高度
2. AVL Tree 平衡二叉树
AVL树是一个用来增加二叉搜索树的所搜效率(通过增加平衡性)并且减小平均搜索高度。
2.1 基本概念
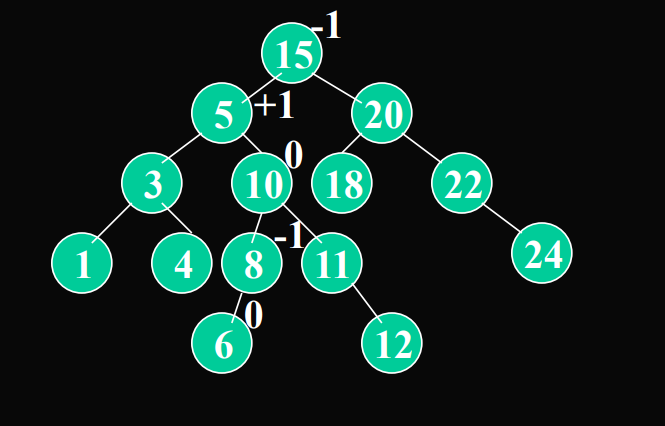
定义:
- AVL树是一个二叉搜索树
- 对于每一个结点,其左子树和右子树的高度之差不超过1
AVL树高:从根节点到每一个叶节点之间的所有路径的最长的一条
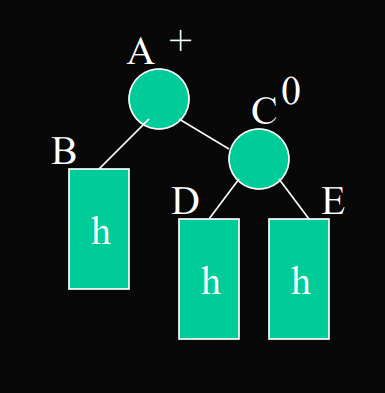
节点x的平衡因子 = x的右树的高度-x的左树的高度
AVL的高度是O(log2n)的,所以搜索的算法复杂度也是O(log2n)。
2.2 插入
- 抽象得看,每个AVL树都大概可以看成这个样子
2.2.1 算法说明
如果没有失衡(没有结点的平衡因子的绝对值大于等于2),那就不需要旋转。
左旋和右旋只会涉及三个结点:失衡节点,失衡节点的某一子节点
左右双旋和右左双旋只会涉及三个结点:失衡节点,失衡节点的某一子节点,失衡节点子节点的某一子节点。
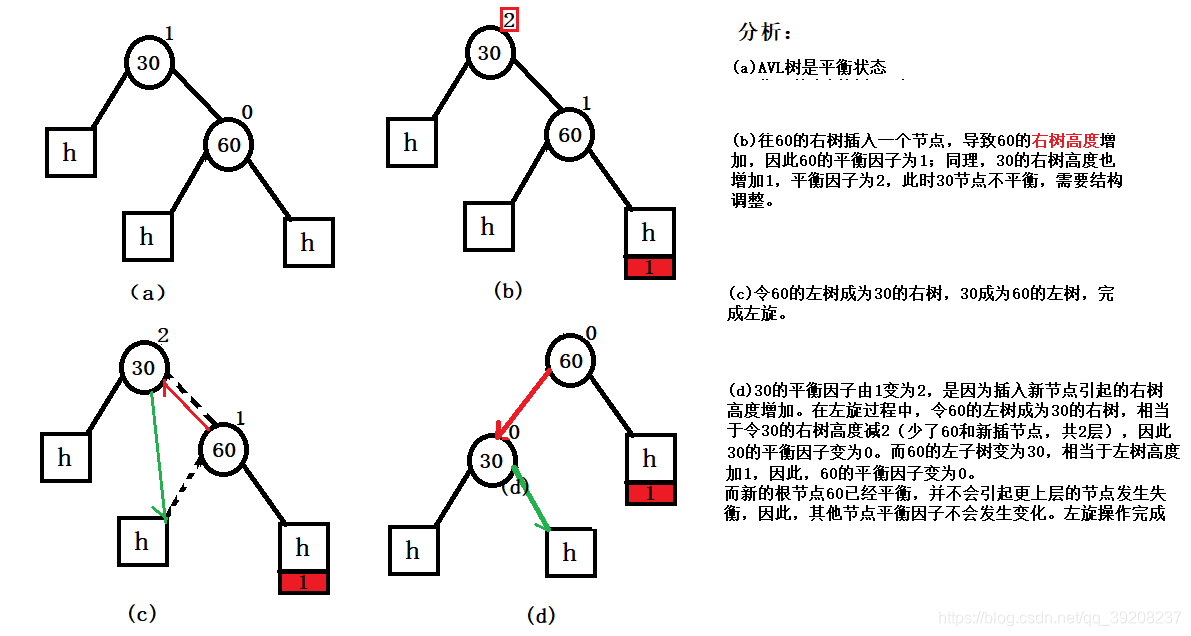
2.2.1.1 左旋
左旋的条件:
从插入的结点一路向上找,找到的第一个失衡结点的平衡因子为2,该失衡节点向下的第一个子结点的平衡因子为1。
左旋的算法:(如上图)
- subL->right = ptr->left
- prt->left = subL
- ptr->bf = sub->bf = 0(调整平衡因子)
2.2.1.2 右旋
右旋的条件:
从插入的结点一路向上找,找到的第一个失衡结点的平衡因子为-2,该失衡节点向下的第一个子结点的平衡因子为-1。
右旋的算法:(如上图)
- subR->left = ptr->right
- ptr->right = subR
- ptr->bf = subR->bf = 0
2.2.1.3 左右双旋
- 左右双旋的条件:
- 从插入的结点一路向上找,找到的第一个失衡结点的平衡因子为-2,该失衡节点向下的第一个子结点的平衡因子为1。
- 左右双旋的算法:(如上图)
- 对于那个平衡因子为1的结点,和它的子结点来一次左旋
- 对于那个失衡结点,与(1)中的子节点,来一次右旋
2.2.1.4 右左双旋
- 右左双旋的条件:
- 从插入的结点一路向上找,找到的第一个失衡结点的平衡因子为2,该失衡节点向下的第一个子结点的平衡因子为-1。
- 左右双旋的算法:(如上图)
- 对于那个平衡因子为1的结点,和它的子结点来一次右旋
- 对于那个失衡结点,与(1)中的子节点,来一次左旋
2.2.2 代码实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
private AVLNode insert( Comparable x, AVLNode t ) {
if (t == null)
t = new AVLNode( x, null, null );
else if ( x.compareTo(t.element) < 0 ){
t.left = insert(x, t.left);//不仅x插入左子树,而其左子树已经调平衡了,也就会子树已经旋转过了
if(height(t.left) – height(t.right) == 2 )
if(x.compareTo(t.left.element)<0)
//根据大小进行调整
t = rotateWithLeftChild (t);//左子树的左子树,只要做一次左向单旋
else t = doubleWithLeftChild(t);//左子树的右子树,需要做一次左右双旋
//下面是对称的插入在右子树上
}else if(x.compareTo(t.element)>0) {
t.right = insert(x, t.right );
if( height(t.right)–height(t.left)== 2)
if(x.compareTo(t.right.element)>0)
t = rotateWithRightChild(t);
else t = doubleWithRightChild(t)
}else;
t.height = max(height(t.left), height(t.right)) + 1;
return t;
}
左旋:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
private static AVLNode rotateWithRightChild(AVLNode k2){
AVLNode k1 = k2.right;//k1持有k2的右子树
k2.right = k1.left;//k2的右子树挂到k1的左子树上
k1.left = k2;//把k2自己挂到k1的左子树上
k2.height = max(height(k2.left),height(k2.right)) + 1;
k1.height = max(k2.height,k1.right) + 1;
return k1;
}
右旋:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
private static AVLNode rotateWithLeftChild( AVLNode k2 ) {
AVLNode k1 = k2.left;//k1持有k2的左子树
k2.left = k1.right;//k1的右子树挂到k2的左子树上
k1.right = k2;//把k2自己挂到k1的右子树上
k2.height = max(height(k2.left), height(k2.right)) + 1 ;
k1.height = max(height(k1.left), k2.height) + 1;
return k1;
}
左右双旋:
1
2
3
4
private static AVLNode doubleWithLeftChild( AVLNode k3 ) {
k3.left = rotateWithRightChild(k3.left);
return rotateWithLeftChild( k3 );
}
右左双旋:
1
2
3
4
private static AVLNode doubleWithRightChild(AVLNode k3){
k3.right = rotateWithLeftChild(k3.right);
return rotateWithRightChild( k3 );
}
2.3 删除
方法 : 与二叉搜索树的删除方法一样。
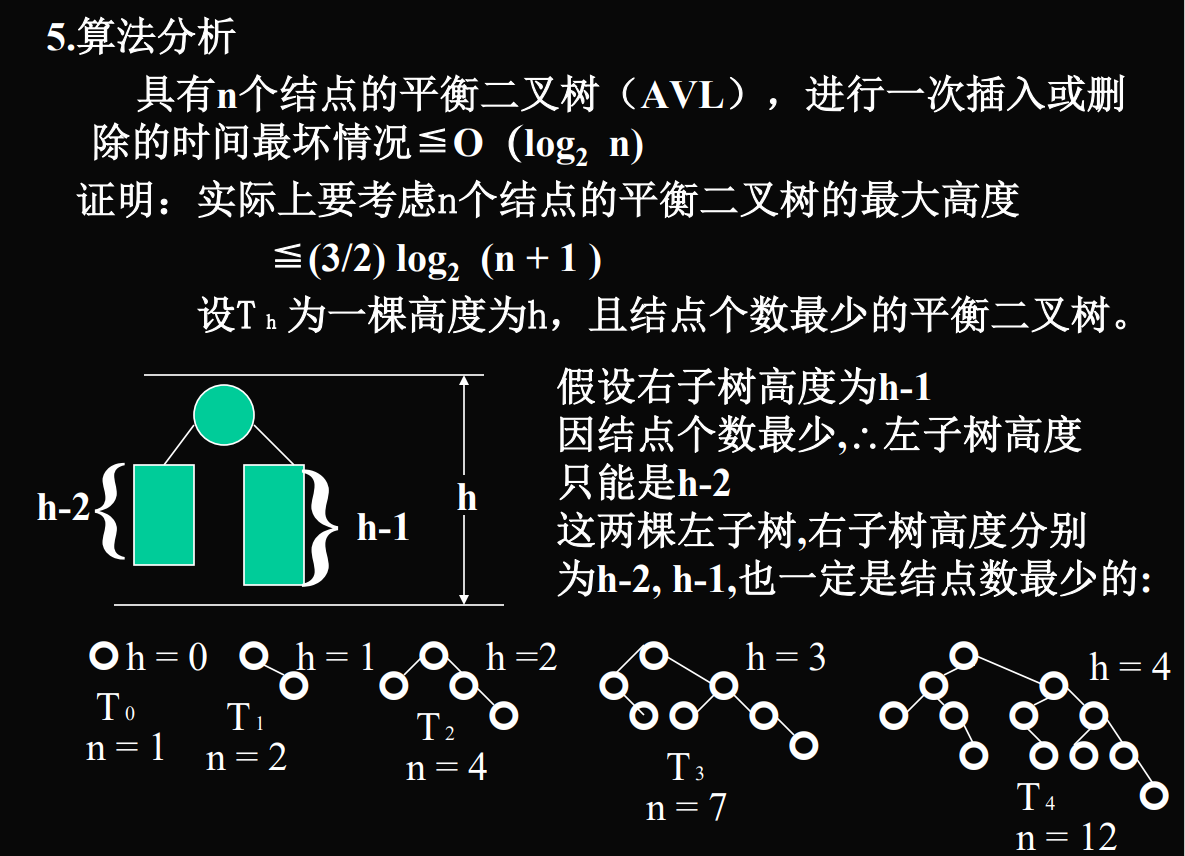
2.4 算法复杂度分析(不做要求)
具有n个结点的平衡二叉树(AVL),进行一次插入或删除的时间最坏情况<= O(log2 n)
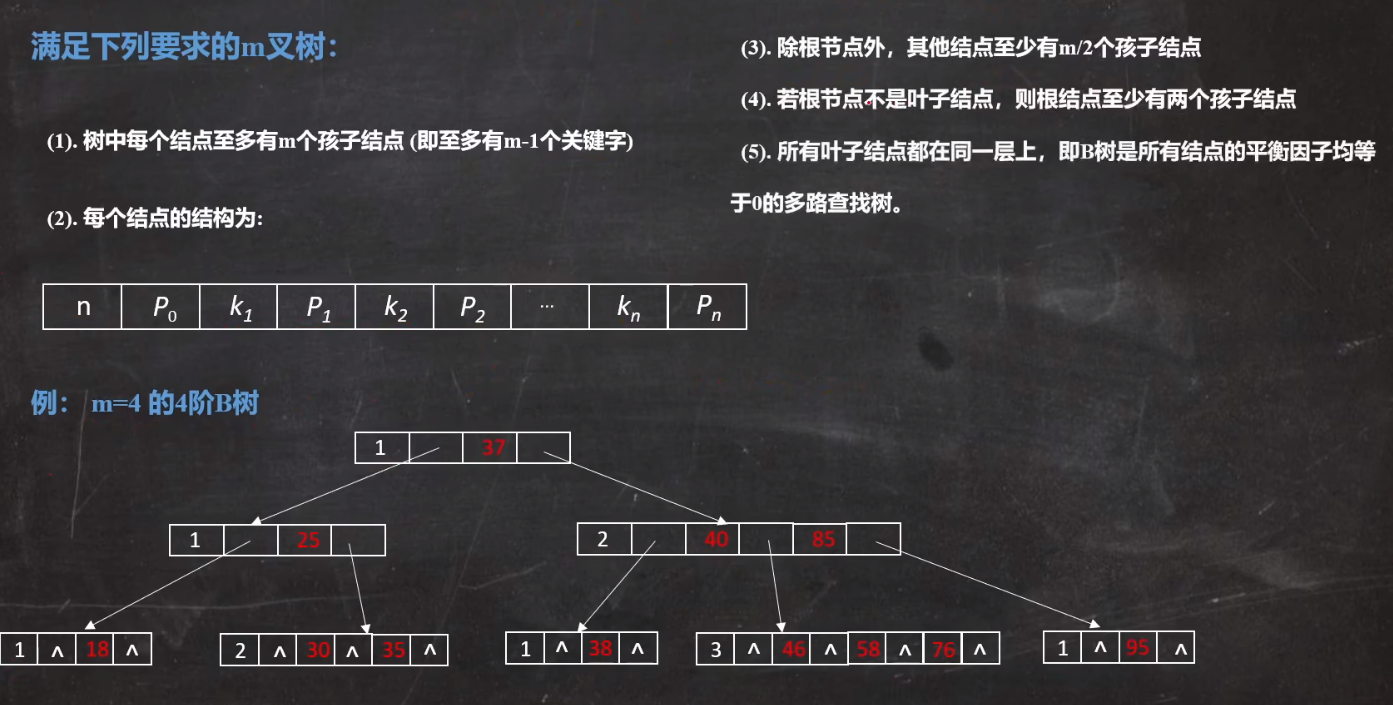
3. B-TREES
3.1 m叉搜索树
3.1.1 定义
3.1.2 操作
3.1.2.1 插入
- 如果一层没有满,就在同一级进行插入。(针对的是m叉的情况)
- 如果这一层已经满了,那么在下一层进行插入。
3.1.2.2 删除
3.1.2.3 m叉搜索树的行高
- 一个高为h的m路搜索树最少有h个结点(每一层只有一个结点),最多有mh-1个结点
- logm(n+1) <= h <= n
3.2 平衡的m路搜索树——B树
3.2.1 定义
- m阶的B树是一个m叉搜索树。如果B树不为空,则B树有相应的扩展属性:
- 根结点至少有两个子女
- 所有非叶子结点的结点都至少有m/2(向上取整)个子结点
- 所有的叶子结点必须都在同一层
- 除根节点外,其它节点都包含 n 个key,其中 m/2(向上取整) -1 <= n <= m-1
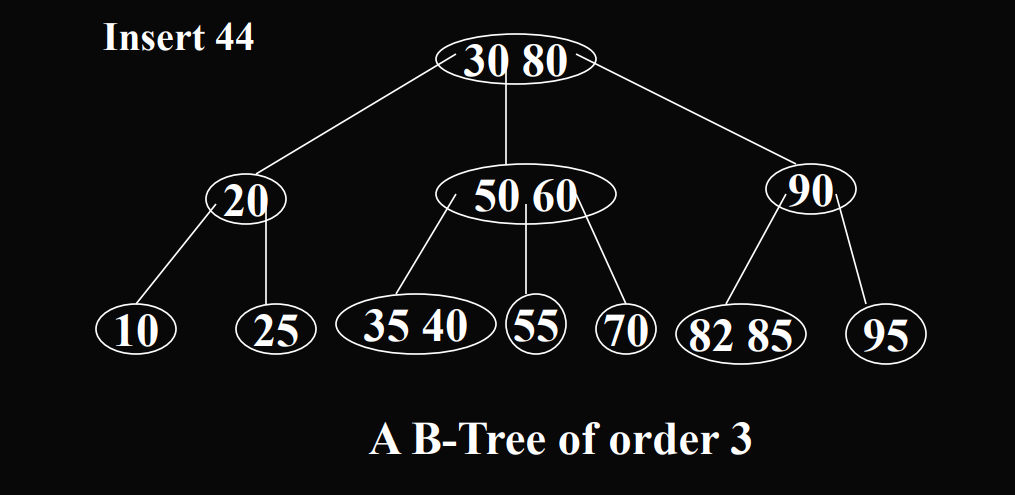
解释:这要从B树的生成开始说起。具体以一颗4阶树来展示B-tree的插入过程。
首先我们 插入 200,300,400,没有什么问题,直接插入就好。
200 300 400 现在我们接着插入500
200 300 400 500 这个时候我们就需要分裂,将中间的key上移到父节点,左边的作为左节点,右边的作为右节点,如下图所示:
此时就可以相通性质2了,如果根节点不是叶子节点,那么它肯定发生了分裂,所以至少会有2个子节点。
同样我们接着插入600,700,800,900插入过程如下图所示:
现在根节点也已经满了,如果我们继续插入910,920,会怎样呢?根节点就会继续分裂,树继续向上生长。看下图:
通过整个的插入过程我们也会发现,B-tree和二叉树的一个显著的区别就是,B-tree是从下往上生长,而二叉树是从上往下生长的。
首先我们知道子节点的个数是等于key的数目+1,然后一个节点达到m个key后就会分裂,所以分裂后的节点最少能得到 m/2 - 1个key 。为啥还要减一呢?因为还要拿一个作为父节点。所以这个节点最少会拥有 m/2 - 1 + 1 = m/2 个子节点。
因为最少有m/2个子节点,所以最少就含有m/2-1个key,m 阶树,每个节点存到了m个key就会分裂,所以最多就有 m-1个key。
3.2.2 性质
- 所有的叶子结点都有相同的层数
- 叶子节点的个数等于关键字个数+1
3.2.3 搜索算法
B树的搜索算法和m叉搜索树的搜索算法是一样的。
3.2.4 插入算法
B树的插入问题经常发生在叶子结点的上一层
思想:
做插入的时候优先插入叶节点:
- 如果叶节点还没有满的时候,直接插入即可
- 如果叶节点已经满了的时候,会进行分类,将中间节点的一个值拉到上级结点(这个结点在中间)。
插入到一个有满子结点的节点中,比如25插入上面那个例子中,满了的节点会分裂成两个节点,就是把中间的提升,将剩下的裂开
3.2.5 删除算法
首先判断删除的关键码是否都在B树中,不在的话直接退出。
判断本结点的key数量是否大于m/2(向上取整) -1,如果是直接删除这个key
如果本结点的key数量小于等于m/2(向上取整) -1
- 兄弟结点的key数量大于m/2(向上取整) -1,从父节点中要一个key,然后由兄弟节点补一个key到父节点
- 如果兄弟结点的key数量小于等于m/2(向上取整) -1
- 如果父节点的key数量大于m/2(向上取整) -1,从父节点要一个下来,然后兄弟合并即可
- 如果父节点的key数量小于等于m/2(向上取整) -1,先从父节点要一个key,然后以父节点为新的当前节点递归。如果到根结点都不能满足其他条件,只能将树的高度-1.
e.g.
3.2.6 B树的结构
- S是节点的元素的个数
- ei</sub是key,按照键值升序排列
- Ci是子树结点